Clark's Grebe
General Description
Clark's Grebes are large and slender with long necks and long, thin bills. Their plumage is dark gray above and white below, with a clear color division. The top of the face is black and the bottom white. In Clark's Grebe, the black does not extend below the eye. In the closely related and similar-appearing Western Grebe, the black ends below the eye. The bill of Clark's Grebe is bright yellow to orange-yellow.
Habitat
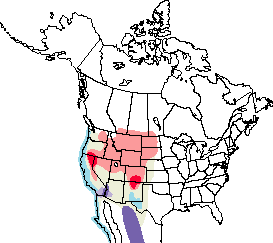
In winter Clark's Grebes are found mostly on saltwater bays. During the breeding season they prefer freshwater wetlands with a mix of open water and emergent vegetation. Breeding areas are located in the central arid steppe and Big Sage/Fescue zones that stretch from California north and east to south-central Canada. Clark's Grebes tend to forage farther from shore and in deeper water than Western Grebes. They are commonly found in mixed flocks with Western Grebes, but even in these flocks they tend to associate preferentially with other Clark's Grebes.
Behavior
Clark's Grebes are highly gregarious in all seasons, wintering in large flocks and nesting in colonies. The neck structure of the Clark's Grebe allows it to thrust its beak forward, like a spear, which it does to catch prey. As a family, grebes are known for their elaborate courtship displays. Clark's Grebes and the closely related Western Grebes perform the most spectacular displays of the family, and arguably the most complex known for any birds. The rituals of Western and Clark's Grebes are almost identical; the only difference is that one of many calls differs in the number of notes.
Diet
In all seasons and habitats, the primary food of the Clark's Grebe is fish.
Nesting
Both the male and female build a floating nest made from a heap of plant material anchored to emergent vegetation in a shallow area of a marsh. The female lays three to four eggs, and both parents incubate. Once hatched, the young leave the nest almost immediately and ride on the backs of the parents. Both parents feed the young. Young are plain gray and white, not striped like the young of other grebes.
Migration Status
Birds from the northern part of the population migrate at night to the Pacific Ocean. Others, mainly in the central California valleys, are year-round residents.
Conservation Status
Tens of thousands of Western and Clark's Grebes were killed at the turn of the 20th Century for their feathers. With protection, they have recovered and can now be found breeding in new areas not occupied historically. However, fluctuating water levels, oil spills, gill nets, and poisons such as rotenone (used to kill carp) may have negative effects on the population. When approached by humans, Clark's Grebes will leave their nest, leaving eggs vulnerable to predation and the elements. For this reason, areas frequently disturbed by humans may have low productivity. Even though they are extremely similar and closely related, Western and Clark's Grebes are separate species. Although they breed side by side in the same area, hybrids are surprisingly rare. Clark's Grebes are far less common in Washington than Westerns.
When and Where to Find in Washington
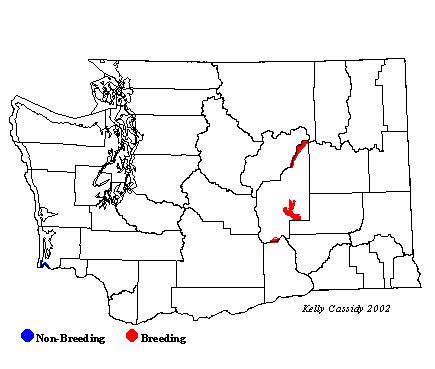
Clark's Grebes are found on both small and large bodies of water in and around Grant County, including Potholes Reservoir, Moses Lake, Banks Lake, and on ponds within the Columbia and Saddle Mountain National Wildlife Refuges. Very rarely, Clark's Grebes are also found on lakes in western Washington in winter.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | ||||||||||||
| Puget Trough | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | |||||
| North Cascades | ||||||||||||
| West Cascades | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||
| East Cascades | R | R | ||||||||||
| Okanogan | ||||||||||||
| Canadian Rockies | ||||||||||||
| Blue Mountains | ||||||||||||
| Columbia Plateau | R | F | F | F | F | F | U | R |
Washington Range Map
North American Range Map